Sedan vs Hatchback? Still Confuse? Read on….
Many hatchback vehicles now cost as much as, if not more than, sedans. However, if you’re planning to buy a car, you should know whether you want a sedan or a hatchback. True, it’s easy to become perplexed. Still, our guide to the Sedan vs Hatchback can help you decide.
Looking back, sedans and hatchbacks were formerly popular among Indian consumers for a long time, at least before the increasing emotion caused by the crossover and SUV segments. There are a dozen various sorts of automobiles in the congested automotive sector; nonetheless, compact cars are more commonly seen on Indian roadways. While it may be simple for you to distinguish between a sedan and a hatchback, do you understand the major differences? Let Auto42 lay down the fundamental differences between sedans and hatchbacks in India and the reasons you would choose one over the other.
What is a Sedan?

The current definition of a sedan is the same as it has always been: a four-door passenger automobile with a separate trunk. A trunk is a completely enclosed cargo storage separated from the passenger compartment by the rear seatback and the fixed package tray beneath the rear window. Many sedans include a fold-down rear seatback that opens into a pass-through to accommodate bulky things that ordinarily fit in the trunk. However, the trunk is walled off from access and prying eyes with the seatback upright.
Sedans have “three-box” bodies: the front box houses the engine, the middlebox is bigger and houses the occupants, and the third box, positioned in the back, houses the trunk. For more than 70 years, they have been the traditional proportions.
What is a Hatchback?

However, determining what is and isn’t a hatchback isn’t that simple. Hatchbacks used to be small, inexpensive, boxy economy cars—Car and Driver created the derogatory name “econobox” to characterize them. They were known as “two-box” automobiles because the engine was in the first box and the passengers and freight were in the second—but there was no trunk. Hatchbacks have two or four doors and a one-piece flip-up tailgate known as a hatch on their squared-off tails. Cars of this kind included early VW Golfs, Renault Le Cars, Ford Escorts, and Dodge Omnis.
Most tiny hatchbacks are far from econoboxes; they’re considerably more beautiful, with elegant rooflines that sweep softly down to their rear bumpers. They’re well-built, frequently tastefully equipped on the inside, and, in some circumstances, far from inexpensive. Mazda 3, Honda Civic Sport, Hyundai Elantra GT, and Toyota Corolla hatchback are examples of modern hatchbacks. Volkswagen has retained the Golf’s squared-off, conventional two-box design, although with a considerably more contemporary look.
The New Generation
On the other hand, Hatchbacks have grown up—way up, into a new type. Several vehicles nowadays appear to be four-door sedans. Still, they feature a rear hatch integrated into their low, elegant roofline that flips up to show a big cargo capacity. These vehicles are often tiny or mid-size sporty or luxury vehicles. Audi A5 Sportback and A7, Buick Regal Sportback, Kia Stinger, and Mercedes-AMG GT53 are the vehicles on the list.

Their lines are seductive, and their roofs slope into what appears to be a tiny trunk. Manufacturers refer to some of these cars as four-door coupes because their low, fastback rooflines resemble two-door sports coupes or sports cars from the past. It may be marketing jargon, but one thing is certain: these racy automobiles are, in fact, hatchbacks.
Sedan vs Hatchback? Let the battle Begin
Sedan vs Hatchback: Capacity for Cargo
Aside from variations in appearance, the most significant distinction between hatchbacks and sedans is seen in their cargo-hauling capacities. A hatchback body shape can hold larger amounts of baggage. It can be loaded and unloaded more readily than a sedan for a given automobile size. Because there is no package tray in the way, the big, flip-up rear hatch door of a hatchback opens to a lofty, unobstructed area.
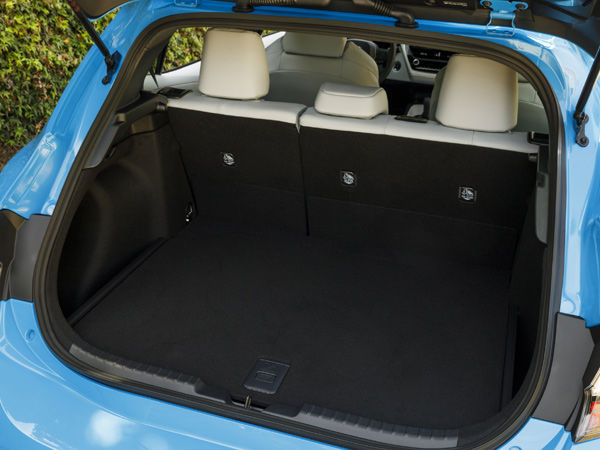

To conceal valuables from view, most hatchbacks include either a solid, swing-up package tray or a soft pull-out cargo-area cover, which are readily removable. Once the rear seat is folded, the big hatch door allows tall, bulky things that would never fit in a sedan’s trunk to be put into the back of the car (virtually all hatchbacks have fold-down rear seats). When the back seat is removed, the hatchback transforms into a mini-SUV.
The size of the things that may be loaded into the trunk of a sedan is restricted by the rear-deck aperture when the lid is opened and the height of the rear package tray, which is fixed in place at the bottom of the back window.
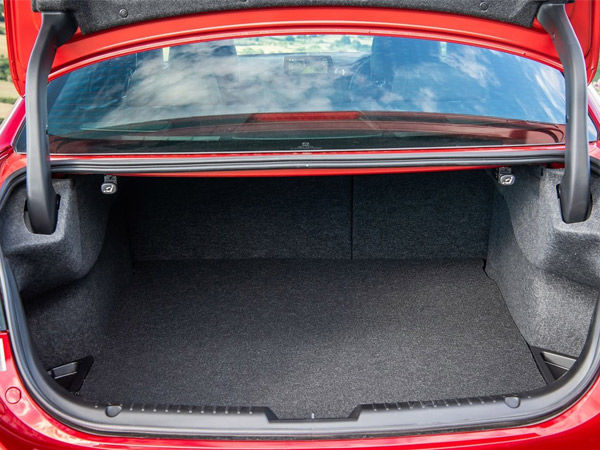

Sedan vs Hatchback: Interior Space
The interior room is another significant distinction between hatchback and sedan vehicles. A sedan’s cabin is usually more extensive than a comparable hatchback, especially for the back passengers. In contrast to a hatchback, which sacrifices some of the room for rear occupants to provide adequate trunk capacity, a sedan includes a separate compartment for carrying baggage. As a result, the inner space at the back remains intact.
So, in most circumstances, sedans are roomier for people than hatchbacks. The sedan should be chosen over the hatchback if you favor passenger space above greater practicality through split seats.
However, one thing to keep in mind here is that hatchbacks do not need to have a tapering roof to have a sporty appearance, which can sometimes limit headroom for rear seats in a sedan. As a result, the hatchback will feel roomier for tall rear occupants than a sedan.
Also Read, Sedan vs SUV: Which should be your Next Car
Sedan vs Hatchback: Dimensions
Naturally, a hatchback is always smaller in size than a comparable sedan. Even when comparing the Swift with the Dzire, the car’s entire length differs by 150 mm. Because the shorter length is useful in congested areas, a hatchback may be a better alternative for purchasers who frequently travel on congested streets.
Furthermore, a hatchback may have a shorter wheelbase than a sedan of the same price, making hatchbacks easier to maneuver than sedans.
Sedan vs Hatchback: Efficiency of Fuel
Hatchbacks and sedans are recognized as among the most fuel-efficient automobiles compared to other car types such as coupes, SUVs, and crossovers. In terms of fuel economy, it is impossible to tell if one is more fuel-efficient than the other because it depends on the model.


Sedan vs Hatchback: Trim & Price Options
Similarly to fuel economy, pricing varies widely depending on vehicle model, with certain hatchbacks being less expensive than sedans and vice versa. On the other hand, Sedans typically have more trim options available due to their popularity over other automobile classes.
So that was our guide to the Difference Between Hatchback and Sedan. We hope it helped you make an informed decision when deciding between the two main automobile body styles. Do you intend to purchase a used vehicle or SUV?